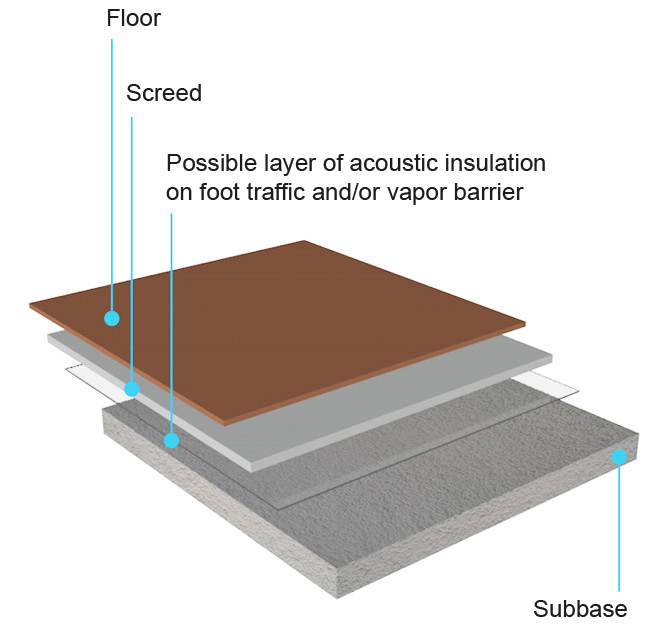
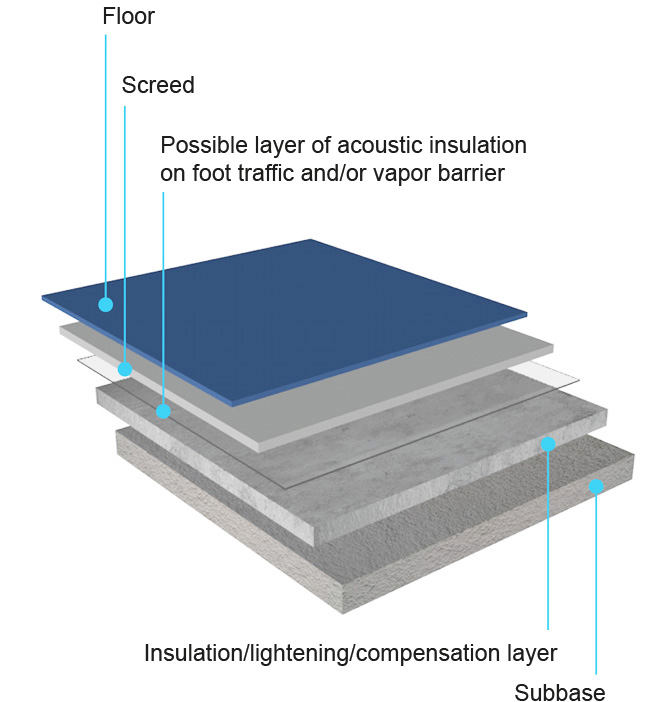
The base is intended to level out any irregularities in the rough structure, to divide the loads transmitted from the floor to the load-bearing structure and to contain, and therefore protect, any pipes, also improving thermal insulation.
Depending on the function and thickness, the base can be single-layer (finishing screed only) or double-layer when the thickness exceeds 10 cm; under the finishing screed there are several layers called insulation and / or lightening and / or compensation layers), depending on the reason for which they have been provided, that is, insulating, lightening or recovering thickness.
Bases: types and features
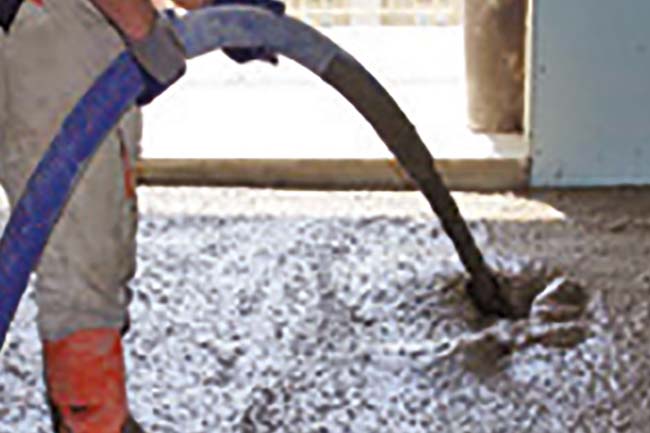 The different types of bases are as follows:
The different types of bases are as follows:
- in sand and cement: this kind is made of sand and cement in appropriate proportions. Used to quickly reach the project height, then to proceed with finishing floor laying;
- self-leveling: this base is special, as it ensures a fair distribution to reach the level of the desired height
- lightened: made of aerated concrete (mix of cement and foaming), or with cement mixed with light material (such as polystyrene, expanded clay, Leka, etc.) guarantees excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. Suitable where radiant heating system is inserted in the floor.
- industrial: it is made with a mix of concrete specifically designed for industrial and logistic flooring buildings, and also yards.
 HAI UNA RICHIESTA?
HAI UNA RICHIESTA? 


